OSHA’s 5 Workplace Hazards
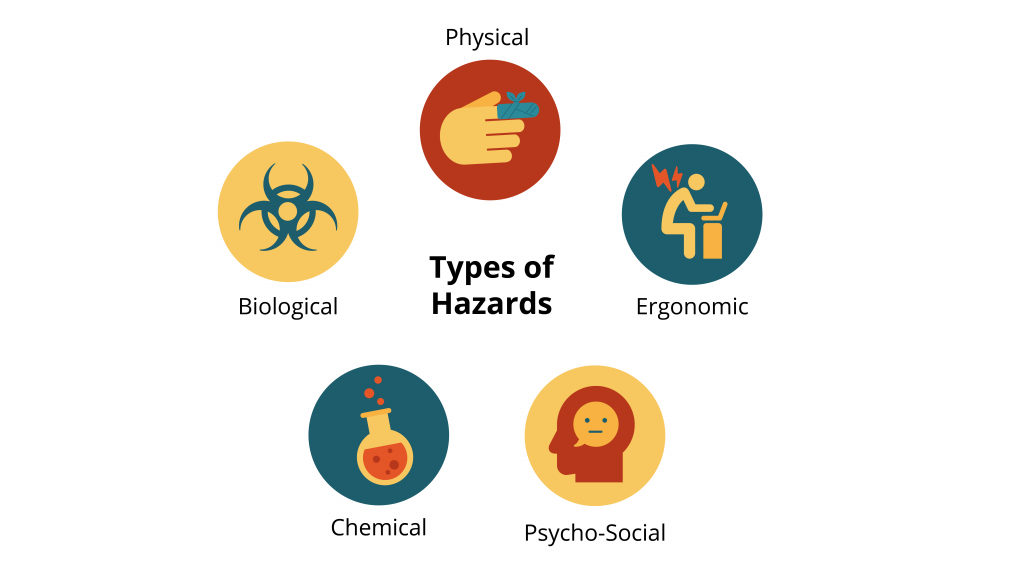
1. Safety Hazards Safety hazards involve any condition, material, or article that can injure workers. In many workplaces, this can include liquid spills on floors, hallways/corridors blocked by boxes, cords, office furniture, and any other material that could trip an employee or hinder a safe and timely building evacuation. Falls from substantial heights, equipment with moving parts, confined quarters, and electrical hazards (such as faulty wiring or overloaded circuits) are a few more examples of OSHA regulations and safety hazards.
2. Chemical Hazards Chemical hazards include non-biological substances that have the potential to cause harm to employee health. Employees can be exposed to chemicals in all forms (liquids, gases/vapors and fumes, and solid particulate materials). Some examples of chemical hazards would be fiberglass, corrosive acids, pesticides and insecticides, fumes from welding, carbon monoxide, and many more.
3. Biological Hazards Biological hazards involve natural materials employees may come in contact with that pose a threat to employee health. Employees working with others, animals, or infectious materials can be exposed to these biological hazards. If they are exposed, protocols need to be in place to protect the employee. Blood, fungi, mold, viruses, and animal droppings are all examples of the types of biological hazards a worker can encounter on the job. We continue to see how dangerous biological hazards can be with regard to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
4. Physical Hazards Physical hazards are hazards that can injure an employee regardless of physical contact or specific proximity. Examples of physical hazards would be radiation, extreme temperature conditions (hot and cold), and consistent sound exposure.
5. Ergonomic Hazards Ergonomic hazards are defined as hazards that cause wear and tear on the body that can likely lead to injury. These workplace injuries can develop over more extended time periods and can often go unnoticed for the majority of their duration. Ergonomic hazards occur when employee work is repetitive, physically limiting, or poses certain strains to the body. Examples of ergonomic hazards would be stress, stationary position, forced posture, and repetitive body movements.
